Android App with Local Nodes
This guide explains how to run the full Interstellar stack locally using Docker or Podman. You will be able to launch the Substrate node, Integritee TEE worker, and IPFS service, then interact with the system using the Interstellar Android demo app.
This setup enables full offline testing without relying on a hosted VPS.
Milestone 4 delivers the transactional layer required to move from secure validation to real economic usage. It introduces a bot-resistant asset distribution system enabling fair token allocations bound to verified human actions, preventing farming and replay abuse. It also integrates fiat on-ramp and off-ramp capabilities, allowing users to seamlessly enter and exit the ecosystem without compromising the security guarantees of the validation protocol. Finally, the milestone implements dynamic fee management across BTC, ETH, DOT, and SOL, automatically adapting transaction parameters to network conditions to ensure reliable inclusion while avoiding overpayment. Together, these components transform the system from a secure authorization mechanism into a complete, transaction environment bridging real-world payments and multi-chain execution.
All features have been extensively tested with a focus on user experience, demonstrating how simple, reliable, and intuitive these flows can be. The current interface has been adjusted to support efficient testing, while leaving room for further UX and UI refinements in the production-grade SDK.
Although the system is not yet production-ready, it provides a robust foundation. Broader edge case coverage, interoperability, and resilience guarantees will be the focus of the upcoming SDK and future milestones. Reviewers are encouraged to focus on the functional flow and experience of the key features in this milestone.
This compatibility note applies to the backend stack, tested on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (x86_64) using Docker (docker-compose) or Podman (with manually installed podman-compose*).
The stack is expected to work on other recent Linux distributions, but this has not been officially verified.
Known issue: May fail on Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3/M4) - due to current SIMD usage and QEMU/Rosetta limitations - crash on M1/M2 (not tested on M3/M4)
The frontend (e.g., Android emulator or physical device) can run on any OS supported by Android Studio (expect some emulator limitations on Apple Silicon)
*Compose tools are required to manage service startup dependencies (e.g., health checks).
1. Prerequisites
| Requirement | Install Guide |
|---|---|
| Docker | Install Docker |
| Docker Compose | Install docker-compose |
curl, wget, jq | Installed via apt/brew or default in most environments |
| Android Studio | Install Android Studio |
ADB (adb reverse) | Comes with Android Studio |
You may also use Podman as an alternative to Docker.
2. Launch the Interstellar Stack Install
The BTC worker connects to a Bitcoin Testnet RPC endpoint using a hosted provider.
For simplicity, we provide curators with a ready-to-use .env file.
Place the file in the same directory as docker-compose.yml.
It contains a single variable:
BITCOIN_TESTNET_API_KEY=<API_KEY_WE_SEND>
⚠️ If you prefer to use your own provider, simply replace the value of BITCOIN_TESTNET_API_KEY in .env.
# Step 1: Create a working directory
mkdir interstellar_m3_demo && cd interstellar_m3_demo
# Step 2: Download the stack config
curl -L -o docker-compose.yml https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Interstellar-Network/containers/refs/tags/testnet-m3/docker-compose.yml
curl -L -o docker-ipfs-init.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Interstellar-Network/containers/refs/tags/testnet-m3/docker-ipfs-init.sh
chmod +x docker-ipfs-init.sh
# Step 3: Place the .env file we send in this directory
# Step 3: Start Docker (if needed)
sudo service docker start # (for most Linux distros)
# Step 4: Launch the stack
sudo docker compose down --timeout 1 && sudo docker compose up --force-recreate
⏳ Waiting for Master Circuit Generation
Once the node and service are running, the system will automatically trigger the generation of master circuits from the hardware description files.
These circuits are compiled using the Verilog logic generated from the original master circuits specifications, processed through the logic synthesis pipeline. This step may take several minutes depending on the environment.
During this time, monitor the logs and wait for the following sequence of messages:
[ocw-circuits] callback_new_skcd_signed sent number : <number> 1-Success - 0-Fail
[ocw-circuits] callback_new_display_circuits_package_signed: (<CID_1>, <message_digits_number>), (<CID_2>, <pinpad_digits_number>) for <account_id>
Shortly before these messages, you will also see large blob uploads to IPFS such as:
Requested started id=<...> method=POST uri=http://ipfs:5001/api/v0/add
These blobs correspond to the master visual circuits (SKCD display circuits), which are the result of the hardware synthesis pipeline. Their appearance in the logs is a strong indicator that the build process has completed.
ℹ️ You can identify this moment easily by spotting two large IPFS file hashes being logged together — one for the secure keypad circuit and one for the display message circuit i.e one time code These hashes will later be used for visual challenge rendering and validation.
Detailed example from integritee_node-1
Requested started id=1059 method=POST uri=http://ipfs:5001/api/v0/add
[fetch_from_remote_grpc_web] content_type: application/json
[ocw-circuits] callback_new_skcd_signed sent number : 1
[ocw-circuits] callback_new_display_circuits_package_signed: ("QmUx8mMo8GgGdUhcgFQVg2sexkVfyq1sViruZiBadUfs4d",2),("QmcwXyZNmLXnjeoA25YSzj41G1sr6ZsHgZZBQVWvcfe1qn",10) for d43593c715fdd31c61141abd04a99fd6822c8558854ccde39a5684e7a56da27d (5GrwvaEF...)
[ocw-circuits] Hello from pallet-ocw-circuits.
🛌 Idle (0 peers), best: #6 (...), finalized #3 (...), ⬇ 0 ⬆ 0
You can also verify the runtime is ready using Polkadot.js
While waiting for the stack to fully initialize, you can explore the architecture and rationale behind
the VCA System Layer. This layer is responsible for producing the VCA Token,
the core cryptographic artifact used by the Trusted Action Validation Protocol (TAVP).
The token is generated through a hardware-secure pipeline starting from VHDL logic descriptions, synthesized into
Verilog and compiled using theYosis and abc logic synthesis toolchain. The resulting master circuits define both the secure display and interaction logic — including the Secure Circuit Descriptor (scd) and its runtime variant, skcd, used for verifiable evaluation.
Once built, these circuits are uploaded to IPFS and used to enable real-time, privacy-preserving visual cryptographic challenges, ensuring each critical user interaction is verifiable and resistant to malware, phishing, and adversarial AI.
3. Install the Android Demo App
Download the APK
From the official Interstellar GitHub Release (specific APKs preconfigured to connect to localhost):
androidApp-arm64-release.apk— for Android devices and Apple Silicon(M1/M2/M3/M4)androidApp-x86_64-release.apk— for Android emulators running on x86_64 platforms (e.g., Windows PCs, Intel-based Mac)
Latest version recommended
While the app runs on Apple Silicon (M1–M4), emulator performance may vary due to ARM virtualization and GPU constraints. For accurate testing—especially for Rust-based rendering and cryptographic logic—choose the best available setup:
| Recommended Option | Notes |
|---|---|
| Mid-to-high-end ARM device | Preferred. e.g., Pixel 5–Pixel 8. Avoid Android 16 (API 36) for now. |
| x86_64 emulator (Intel) | Reliable with mid-range or better GPU. |
| Apple Silicon (M3/M4) emulator | Acceptable if GPU is sufficient. Better than M1/M2 for rendering. |
| Apple Silicon (M1/M2) emulator | Works, but may show degraded performance or rendering issues. |
If you already have an older version of the Interstellar Android app installed, you must uninstall it before installing the M3 build.
The app uses local secure storage and cached configuration; keeping a previous version may lead to inconsistent behavior during transaction signing or validation.
Option 1: Physical Device
- Transfer the APK to your phone or download it directly from the device
- Allow app installation from external sources
- Install the APK
- Connect your devices to Android Studio
Ensure that your device is configured for english language
Option 2: Emulator
- Create a
Pixel 7or equivalent emulatorAPI 31+-API 35 - Edit the emulator and select an API 31+ below the default API 36 (API 34 more stable)
- Launch the emulator
- Drag and drop the APK onto the emulator window to install
Our app currently crashes on Android API 36. The issue is not caused by the new 16KB memory page model, as it runs correctly on API 35 with 16KB pages. API 36 is a very recent release and may introduce subtle runtime or platform-level changes that affect low-level Rust code (e.g., garbled circuit evaluator or frame renderer). Until further investigation, we recommend using API 34 (more stable on emulator) or earlier for testing.
On Apple Silicon (M1–M4), emulators may fail to render or execute low-level native code correctly unless software rendering is enabled.
To enable it:
Device Manager → Edit → Advanced Settings → Emulated Performance → Graphics → Software
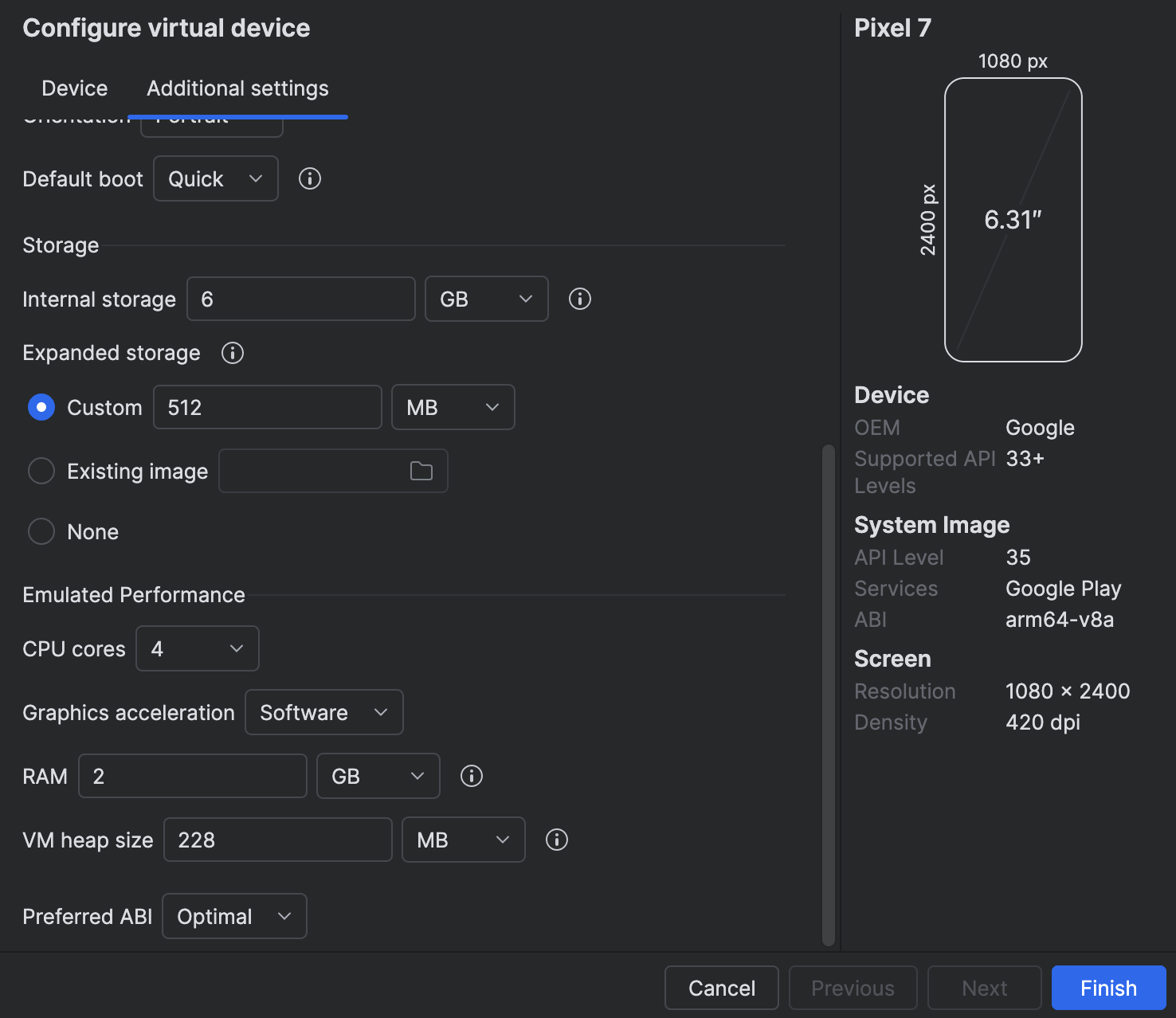
- Mandatory for M1/M2: hardware acceleration is not supported and cause crashes.
- Not tested on M3/M4: may support hardware acceleration, but software mode is safer for compatibility.
Enabling this setting ensures more reliable emulator behavior, especially for native Rust or cryptographic rendering, at the cost of some performance.
2. Link App to your local Interstellar stack:
The Android app is preconfigured to connect to localhost
To allow the Android app to connect to your local blockchain and IPFS stack:
Step 1: adb reverse Setup
On the Desktop connected to the Device or running the Emulator (Windows, Mac OS, Linux)
If Android Studio is already installed, you can enable adb in your terminal by adding it to your PATH with the following command (adjust the path if needed):
Add adb PATH:
Linux:
export PATH=$PATH:$HOME/Android/Sdk/platform-tools
Mac OS:
export PATH="$HOME/Library/Android/sdk/platform-tools:$PATH"
Windows powershell:
$env:Path += ";$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Android\Sdk\platform-tools"
adb reverse tcp:9944 tcp:9944 # Substrate WS
adb reverse tcp:2090 tcp:2090 # Integritee node port
adb reverse tcp:5001 tcp:5001 # IPFS
Make sure adb is properly configured and the emulator or device is detected
with adb devices
You can also check the reverse setup with adb reverse --list
This works for both emulators and real devices connected via USB
Step 2 (optional): ssh Port Forwarding
On the System or VM running the Blockchain stack (WSL2, Remote VM)
If the emulator is running (or the device is connected) on a different network interface than the backend (e.g., the backend runs in WSL2 and the Android emulator or device is connected via USB to Windows), you may need to configure port forwarding between the desktop and the blockchain.
WSL2 -> Windows example:
export WSL_HOST_IP=$(ip route | awk '/default/ {print $3}')
ssh -N -R 9944:localhost:9944 -R 5001:localhost:5001 -R 2090:localhost:2090 [windows_user_name]@$WSL_HOST_IP
To avoid issues with ssh or adb reverse during this local test, you can temporarily disable the Firewall:
Example on Windows with PowerShell (as Administrator):
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain,Private,Public -Enabled False
You can re-enable it later with:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain,Private,Public -Enabled True
During Milestone 4, our primary objective is to validate the backend capabilities required to generate, sign, and execute transactions across different chains.
At this stage, the focus is on ensuring correctness and robustness of the transaction pipeline at the infrastructure level. User-facing aspects such as application UI/UX, visual polish, or cosmetic design are not yet part of the milestone scope. Especially because our focus is the delivery of a mobile SDK.
In addition, while the backend successfully submits transactions, we have not yet integrated state tracking from the backend (e.g., monitoring transaction inclusion and confirmation events). This will be addressed in subsequent milestones, once the foundational backend logic is fully validated.
Secure Asset Distribution — Tutorial
This guide explains how to:
- Create an asset distribution campaign
- Generate shareable claim links
- Let users claim assets (existing wallet or new installation)
The distribution is protected against automation and ensures one allocation per device.
Prerequisites
- Wallet application installed (campaign creator only)
- Sufficient balance to fund the campaign
- Supported network selected
Step 1 — Create a Campaign
Navigate to:
Airdrop Gift Icon �→ Create Campaign + Icom
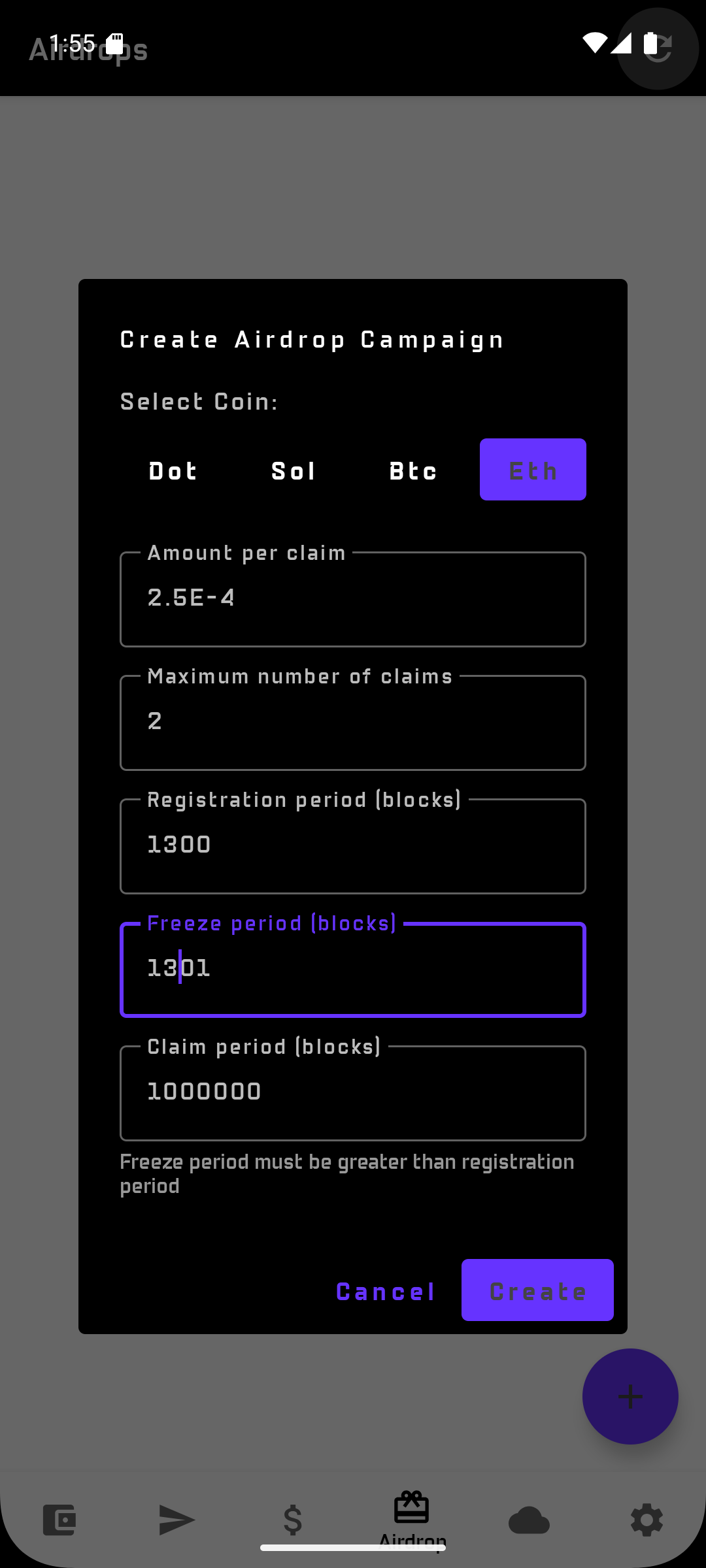
Fill in the parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Asset | Token to distribute |
| Amount per claim | Allocation per participant |
| Claim limit | Maximum number of recipients |
| Registration period | How long registration phase lasts |
| Freeze period | Lock duration after claim |
| Expiration | Campaign closing time |
All period should be define in blocks numbers
- Freeze period should be superiour to Registration period
- A Campaign will move to Closed state if now is superior to Registration period and it was not yet funded
- Default values proposed are choosen to facilitate the testing
Tap Create
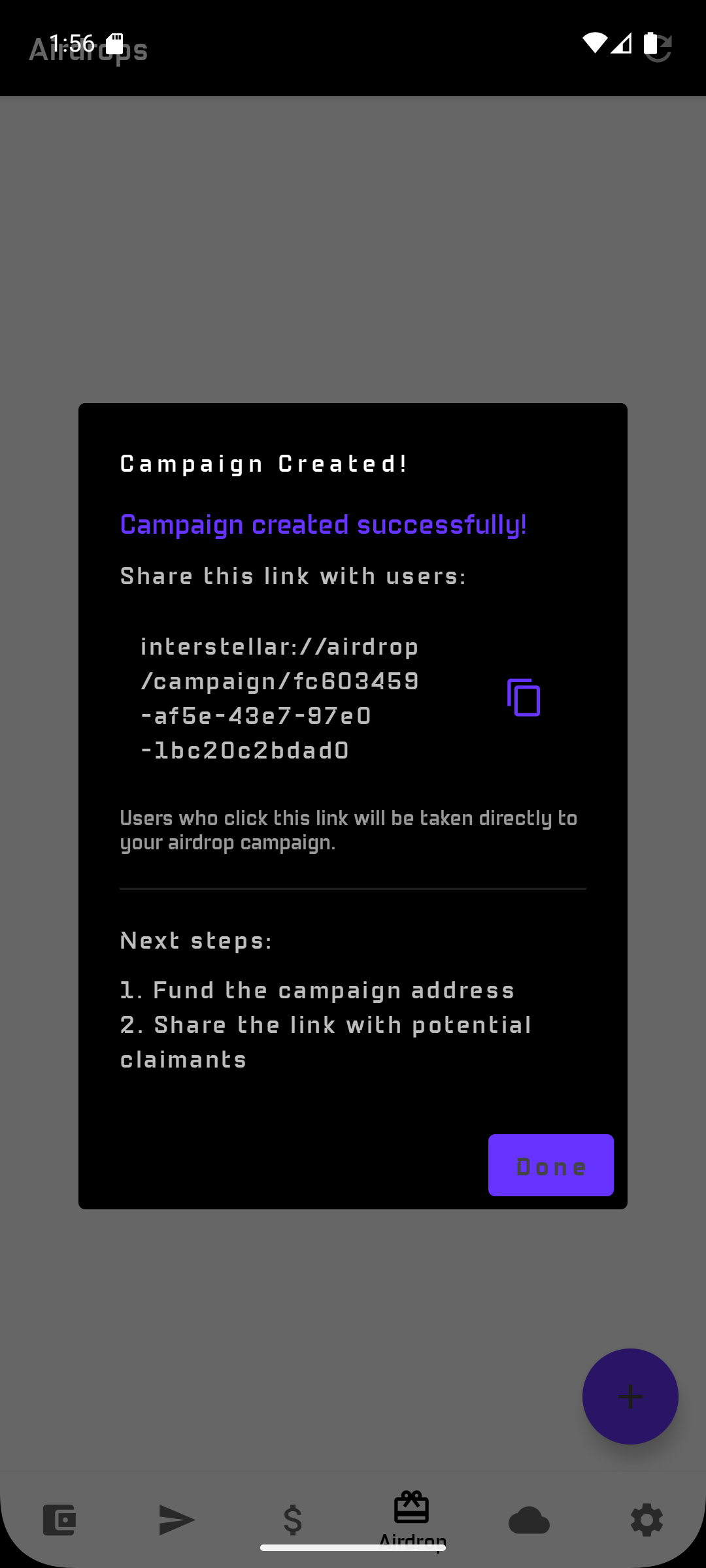
The wallet generates a unique deep link to share with all participants and then a dedicated funding address.
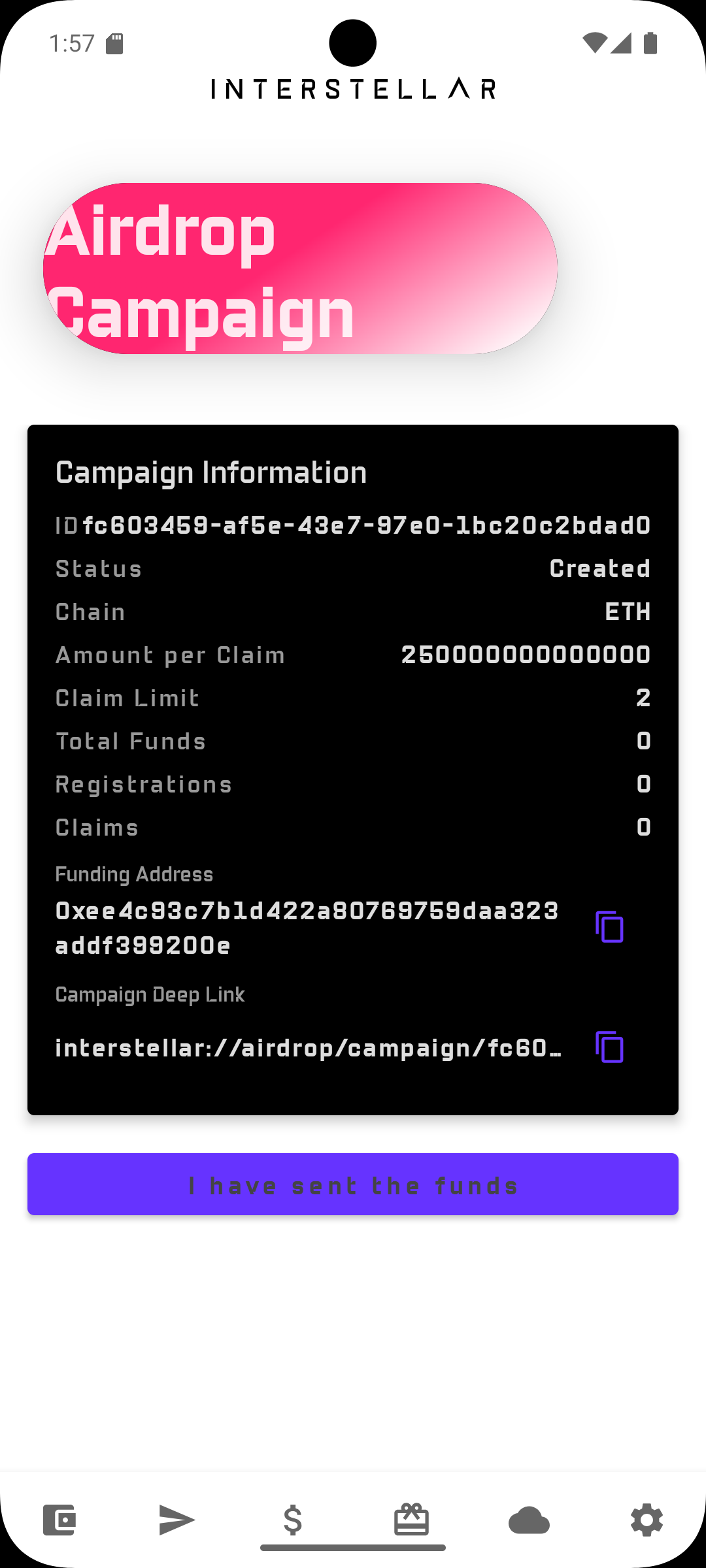
Step 2 — Fund the Campaign
Send funds to the generated campaign address. Once the balance is detected, the campaign becomes Active.
Once the campaign is active you can set-up a recovery (Cloud Icon) for the wallet that created the campaign. The quicker is with an inputed NFC ex: 12345678 and then reset your app (Setting Icon) to simulate a new app
Step 3 — Register to the Campaign
Use the deep link you got during the campaign creation.
You can use the following adb cmd example:
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "interstellar://airdrop/campaign/campaign_ID" gg.interstellar.wallet.android
to provide your app with the link replace the quoted "deep link" with the one you receive during campaign creation
When done the app will prompt you to register with "Register Now" button i.e type a one time code
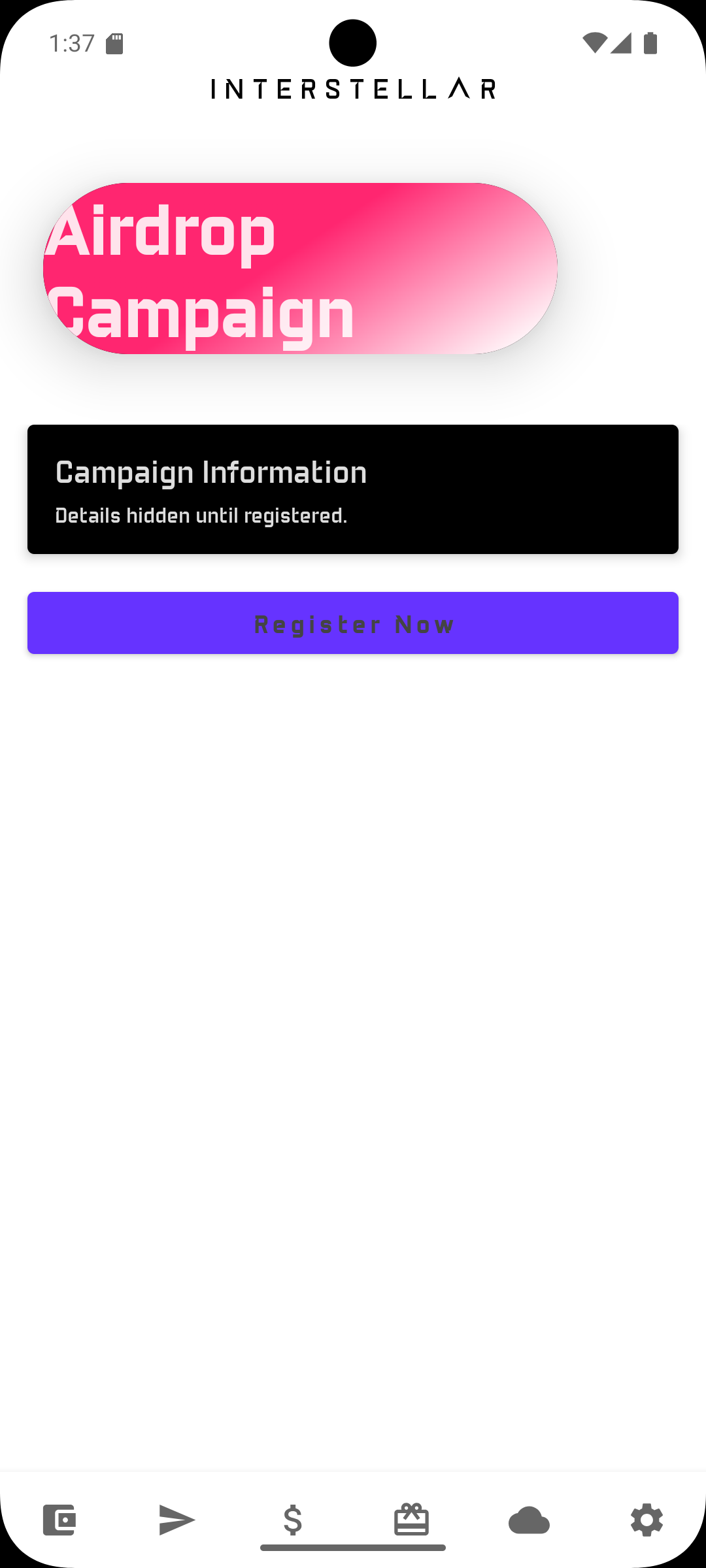

The allocation enters the Frozen state until the freeze period expires.
Step 5 — Claim Assets
You need to wait for the Freeze period to end
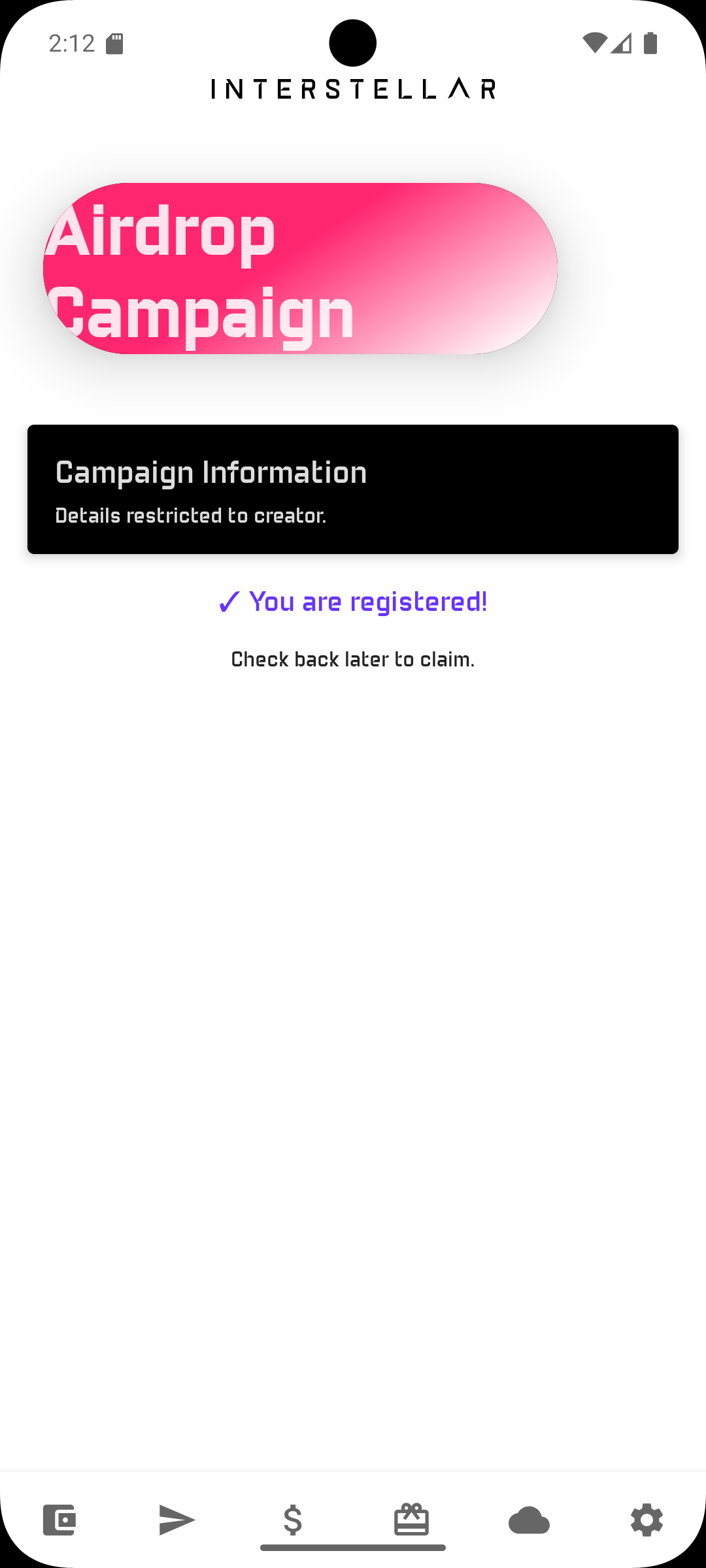
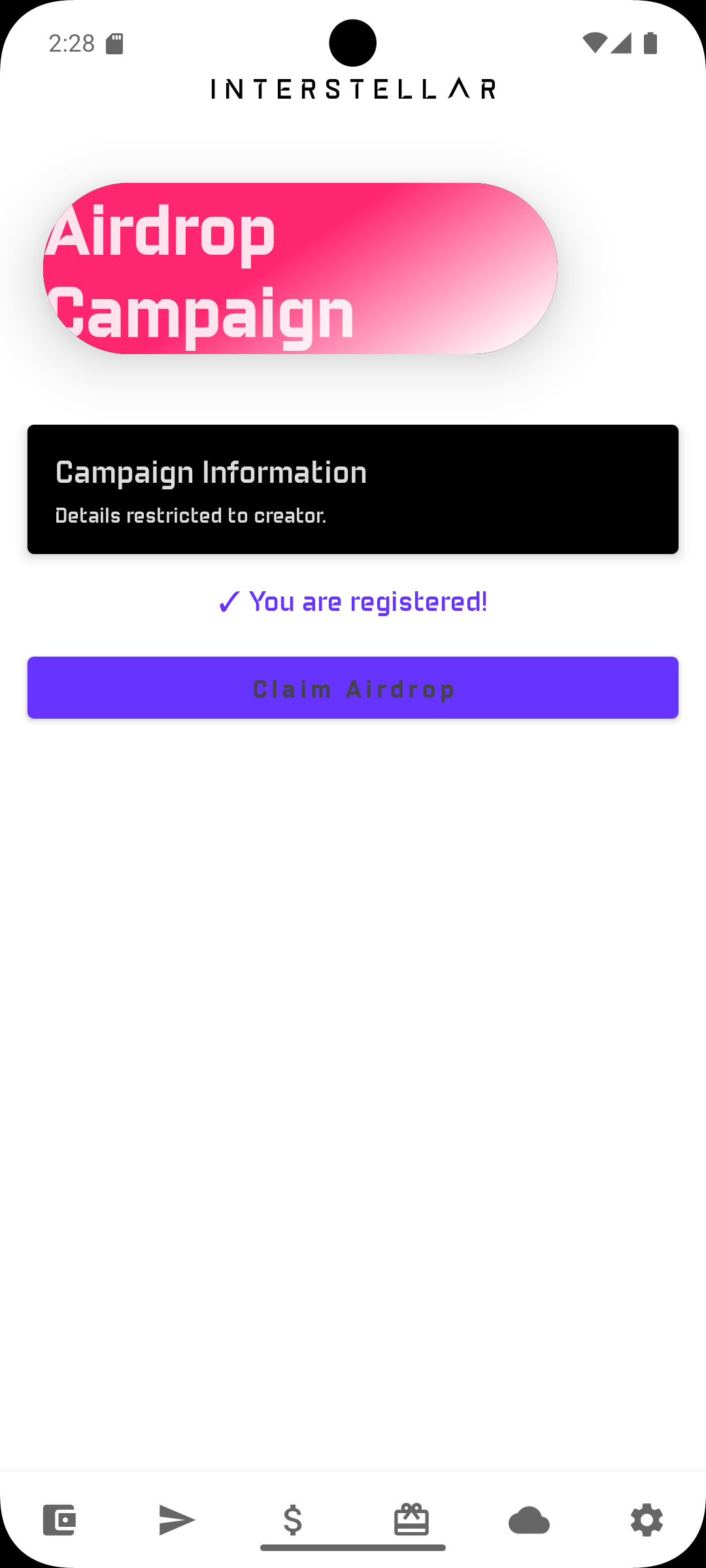
Click on the "Claim Airdrop" button to get your assets when it appears, you will be prompted with a validation screen i.e one time code to input to proceed with the claim.
Campaign Completion
The campaign automatically closes when:
- Claim limit reached
- Expiration reached
- Creator closes manually
You can recover the wallet account associated to the campaign creation using your NFC number (quicker) or the recovery item(s) you have choosen to check the campaign status

Important Rules
- One claim per device
- Reinstall does not allow reclaim
- Recovery blocks claiming
- Funds locked before spending
- Link reuse allowed (not unique)
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Claim refused | Already claimed on this device |
| Cannot unlock | Freeze period not finished |
| Campaign inactive | Not funded or expired |
| Link opens store | App not installed yet |
Result
You have successfully distributed assets securely while preventing farming and automated abuse.
Fiat On-Ramp — Tutorial
This guide shows how to acquire testnet assets directly inside the wallet using the integrated fiat on-ramp.
⚠️ Current environment uses testnet tokens. No real money is transferred.
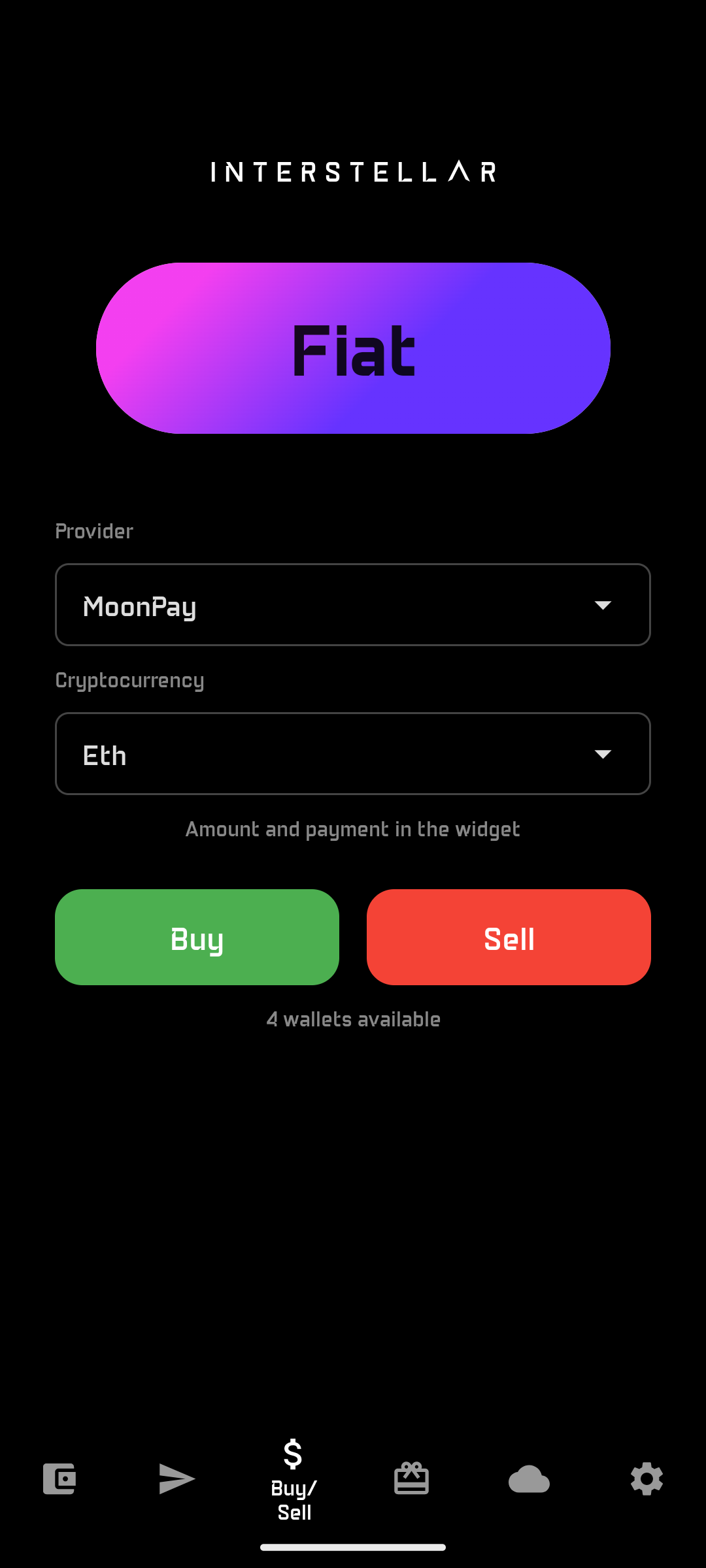
Step 1 — Open Buy Interface
Navigate to:
$ icon → Buy/Sell
Select the desired network and asset.
Step 2 — Choose Amount
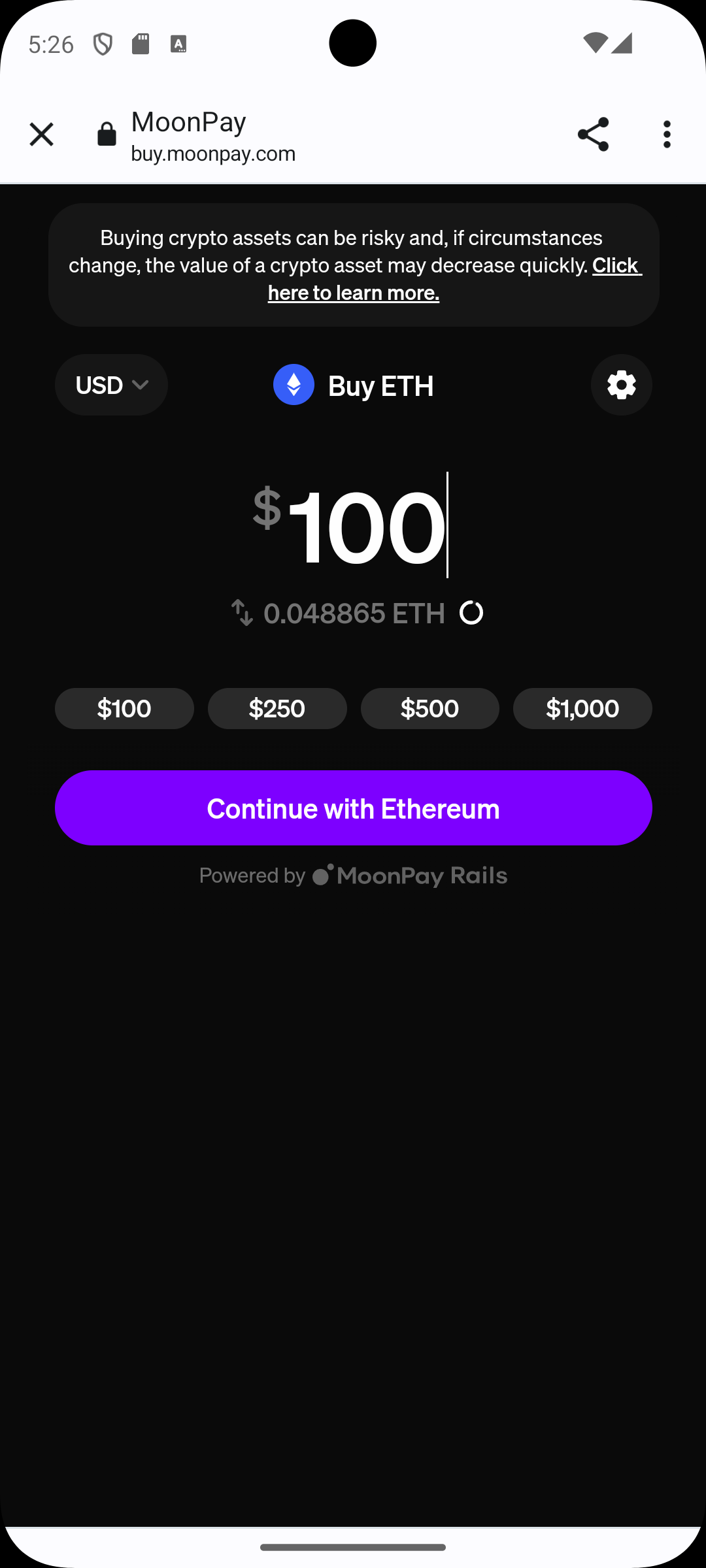
Enter the fiat amount to simulate purchase.
The wallet displays the estimated token amount.
Tap Continue
Step 3 — Registration
You enter now in a registration procees.
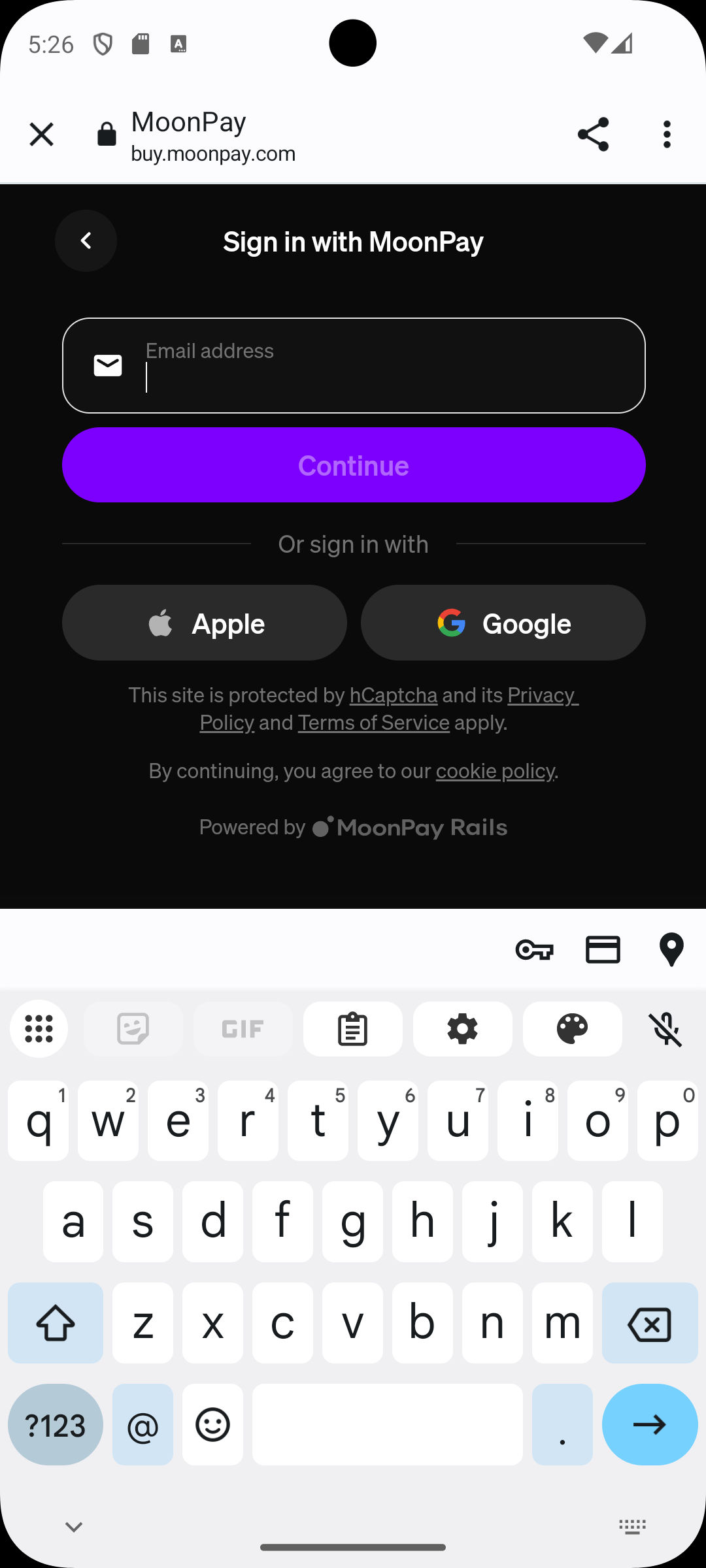
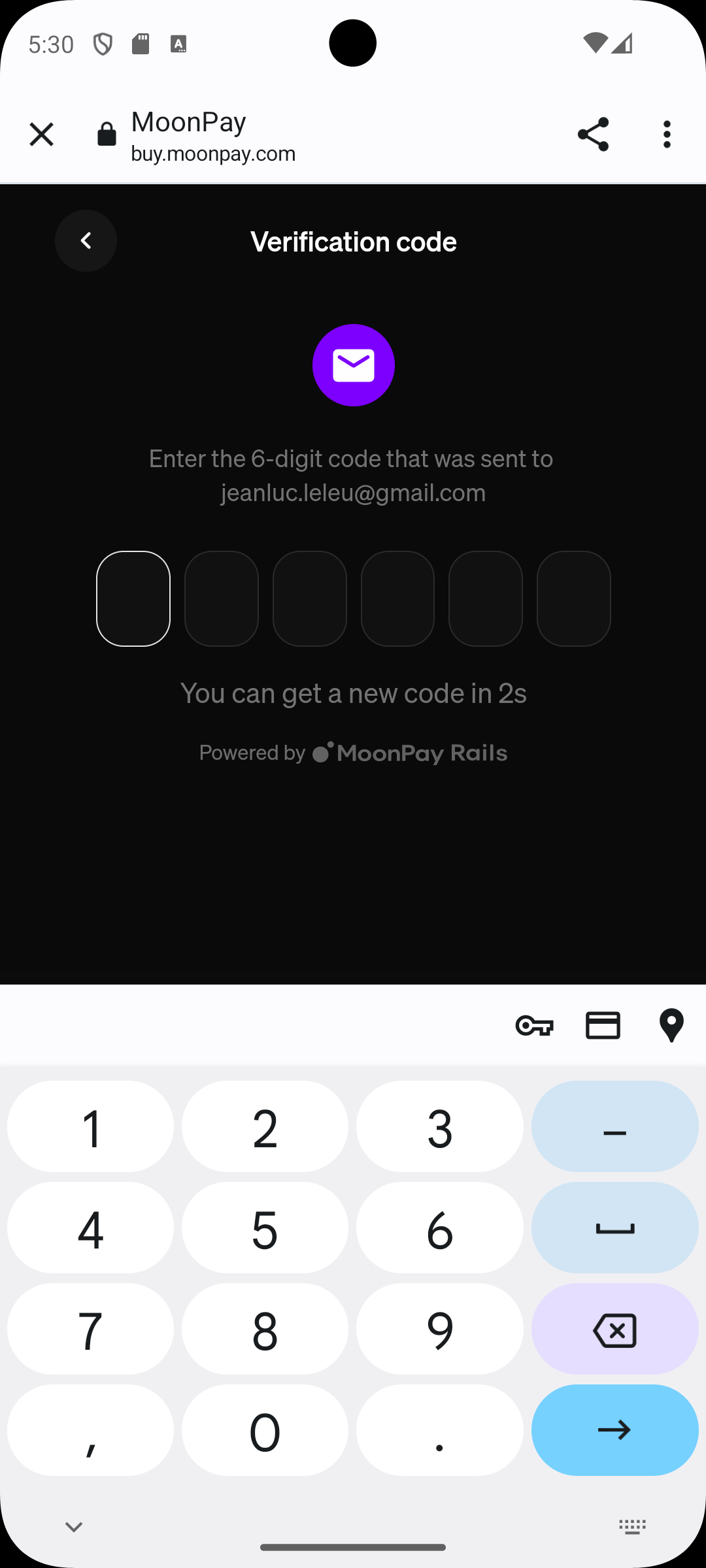
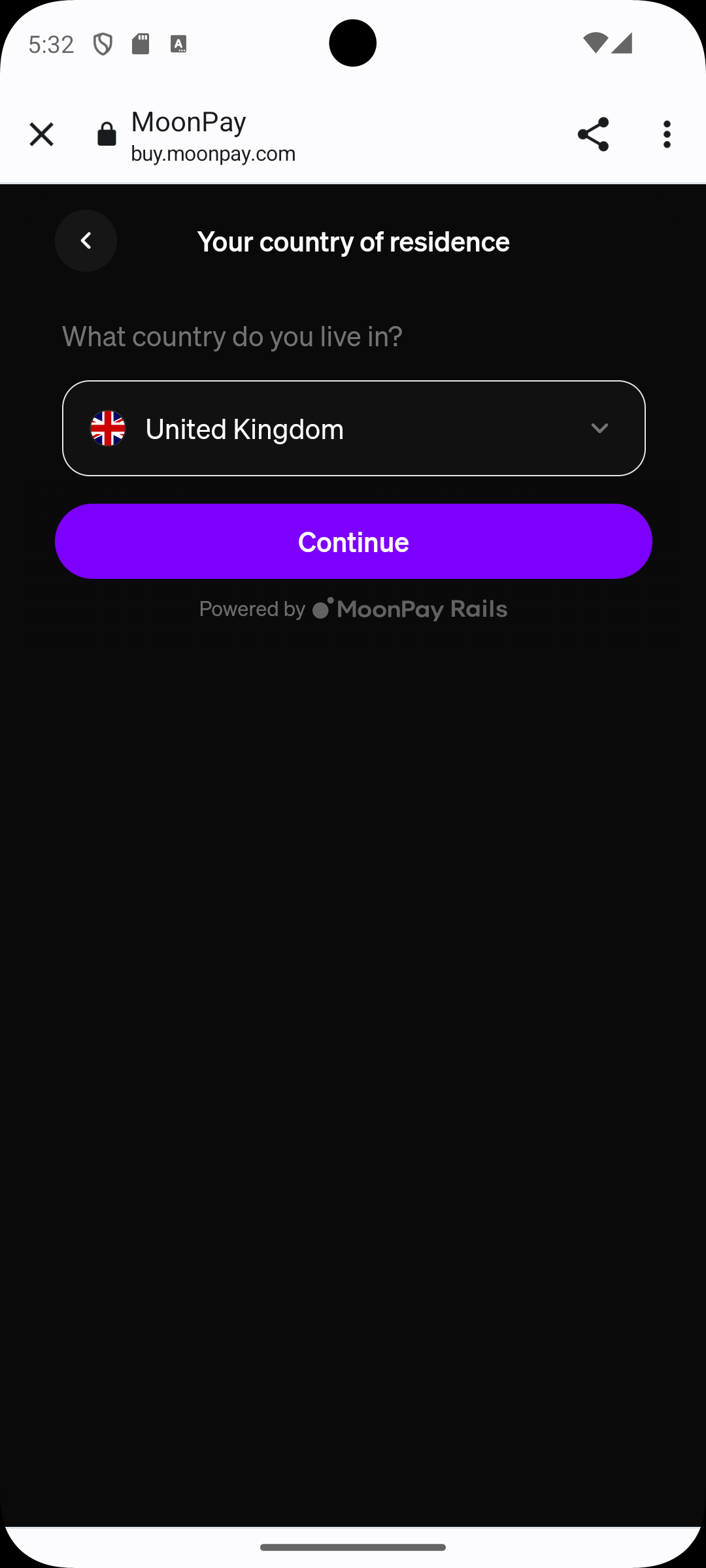
We recommend adding a UK address for sandbox accounts since these work best with our test credit cards.
IMPORTANT: you need to use the "skip" button when asked for photo ID and liveness check
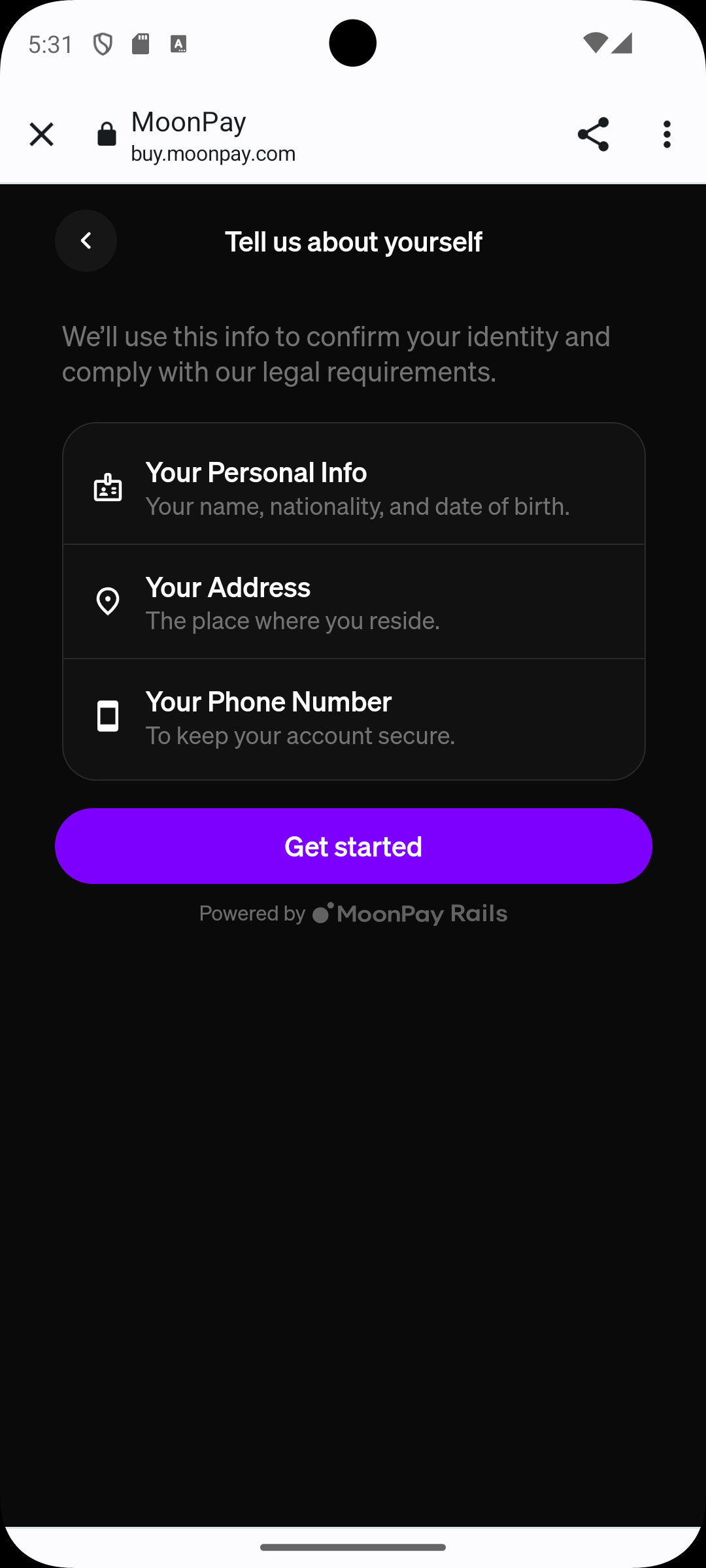
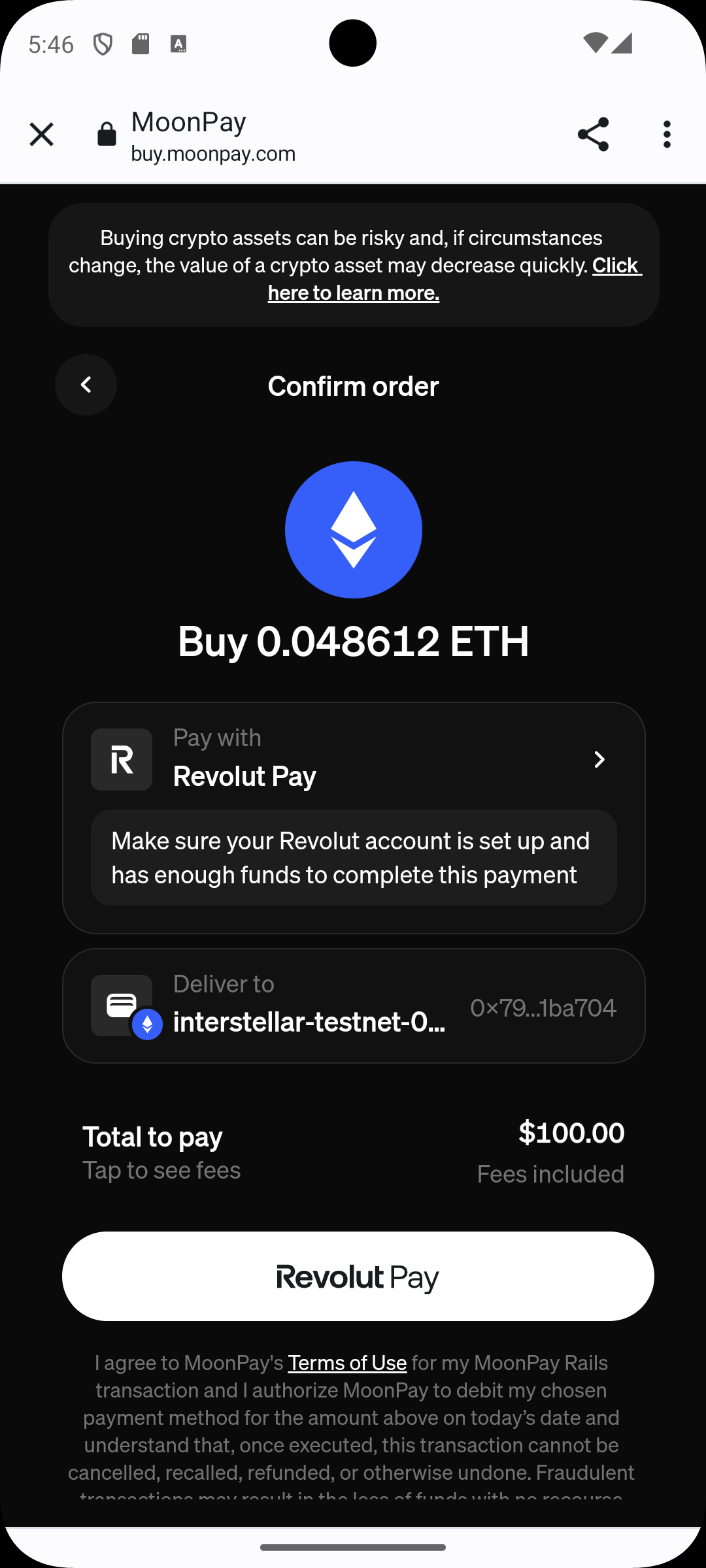
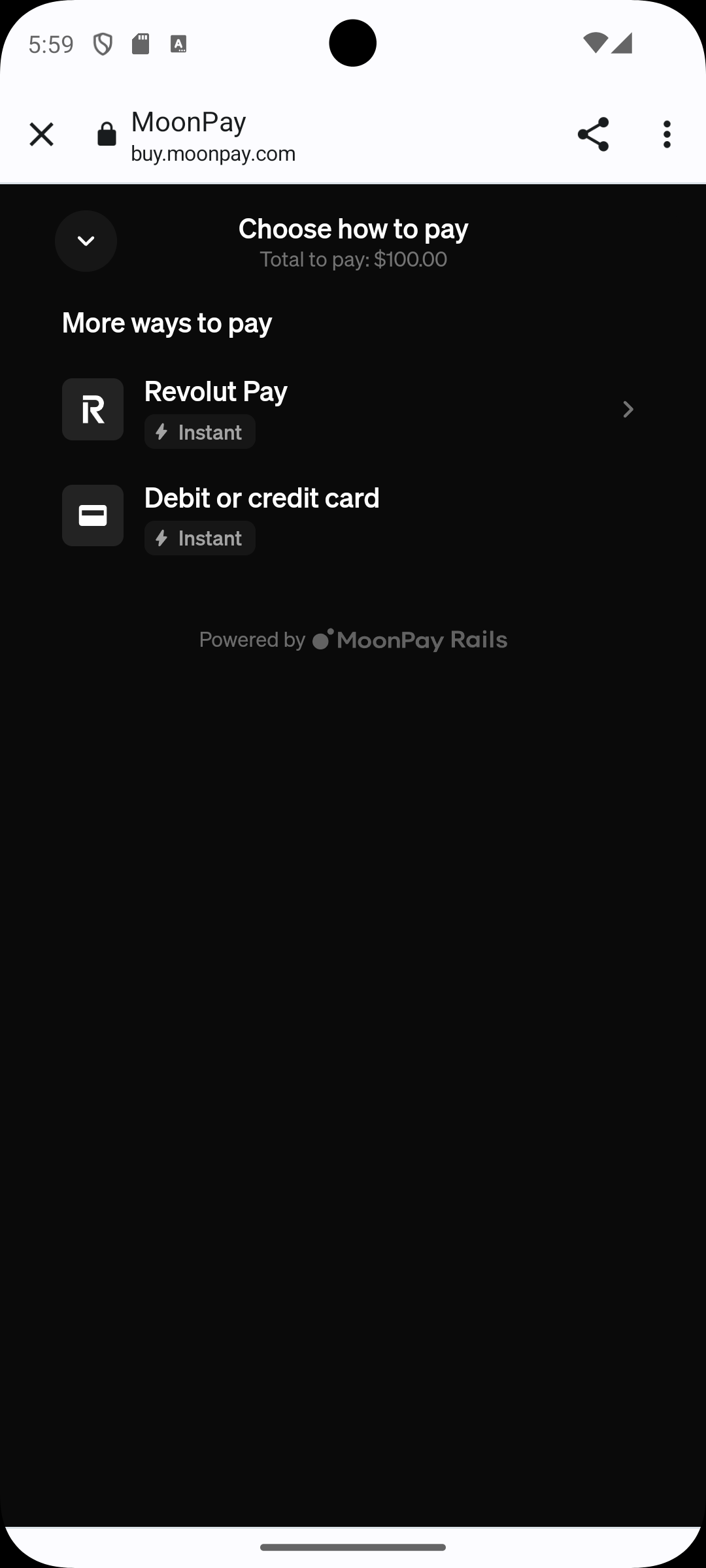
When registration is completed, pay attention to select a debit or credit card instead of revolut
Step 4 — Choose a payment card
Test Card to use (frictionless recomended)
| Card Type | Card Number | Expiration | CVC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visa 3DS Frictionless (UK) | 4485 0403 7153 6584 | 12/2030 | 123 |
| Visa 3DS Challenge (UK) | 4242 4242 4242 4242 | 12/2030 | 123 |
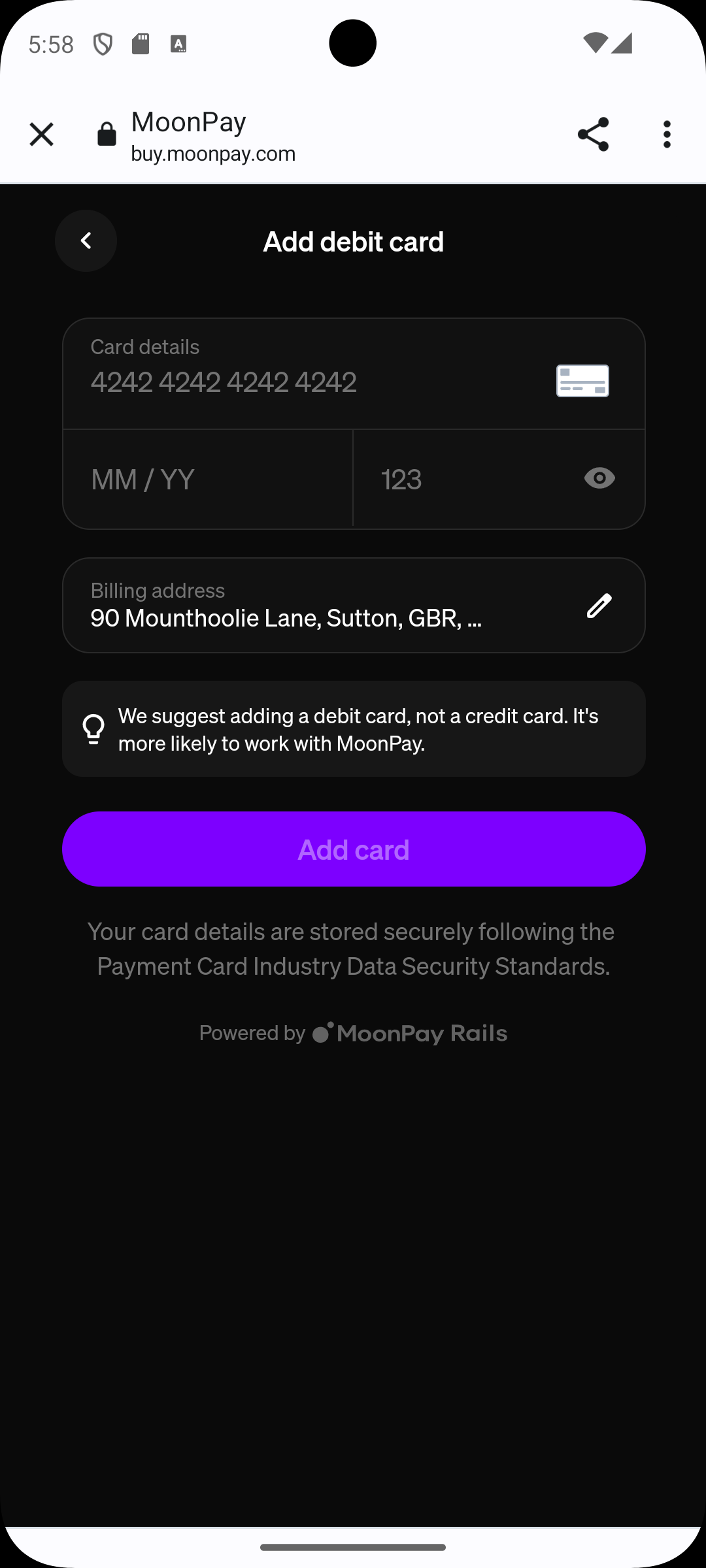
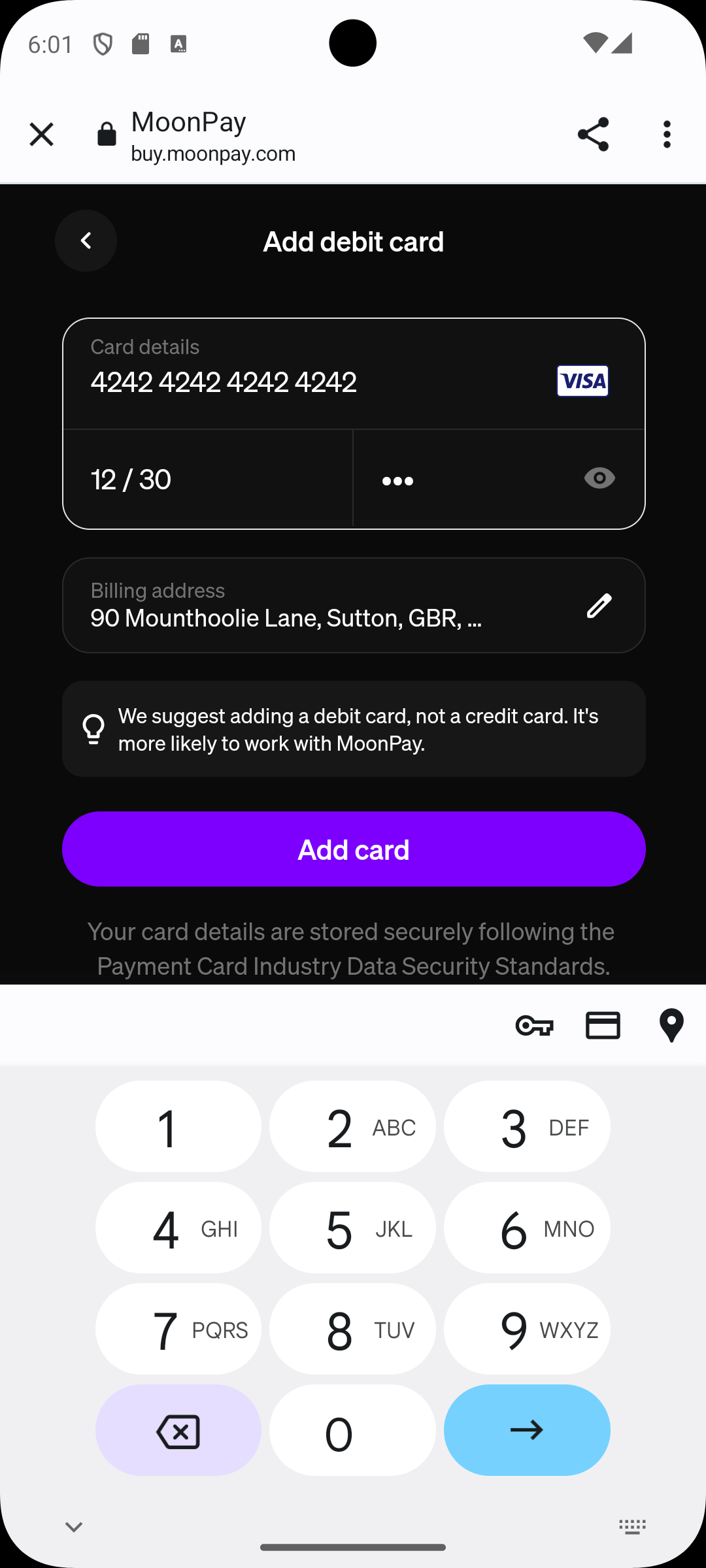
in this example we used the Visa with challenge, it adds an additional control step you can avoid by using the frictionless card.
Step 5 — Provider Confirmation
The payment provider interface opens.
Confirm the transaction.
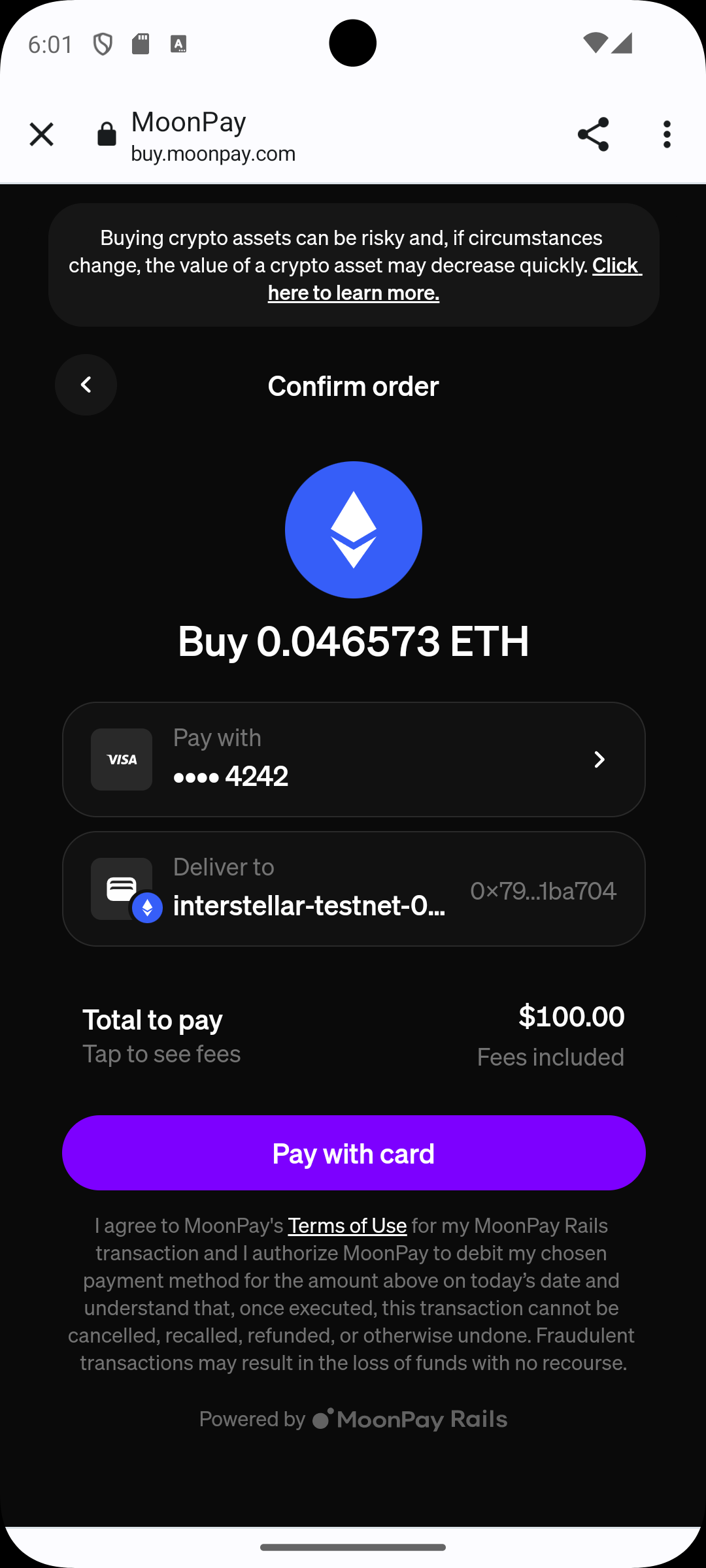
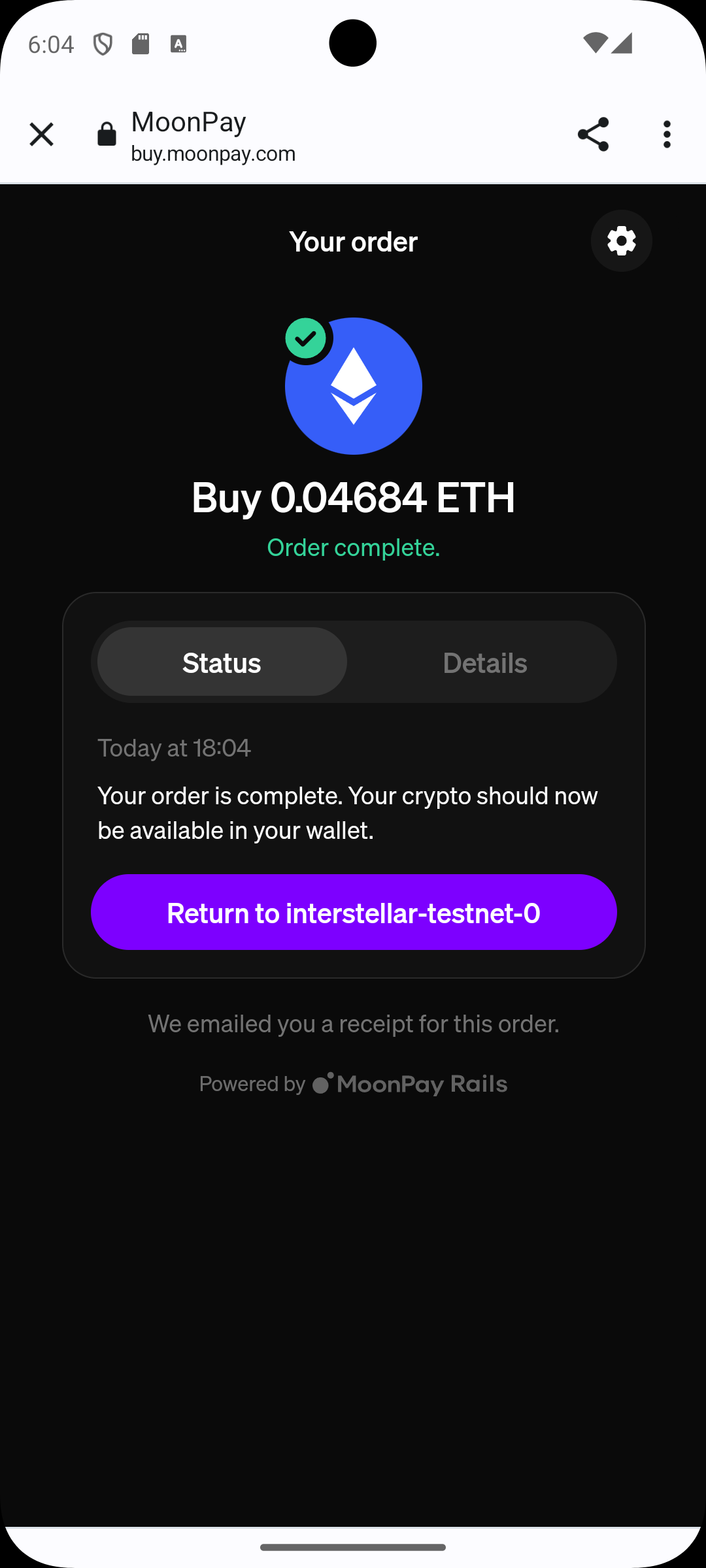
Step 5 — Receive Funds
After confirmation, the assets appear in the wallet balance.
Notes
- Tokens are testnet only
- Settlement is simulated
- Same flow as production environment
You have successfully acquired assets through the integrated on-ramp.
🛠️ Interpreting Logs
Airdrop Campaign — Logs Walkthrough (Create → Fund → Register → Claim)
This page walks through the end-to-end secure asset distribution flow using the ETH campaign captured in the logs as example(that match tutorials screenshot example).
It covers:
- Campaign creation and activation (funding)
- Registration of participants (VCA validation via
pallet_tx_validation) - Transition to claim phase
- Claim (second VCA validation + external transfer)
The same lifecycle applies to DOT / BTC / SOL. Only the asset name (
chain=...) and fee/address specifics differ.
Context: Campaign Identifiers
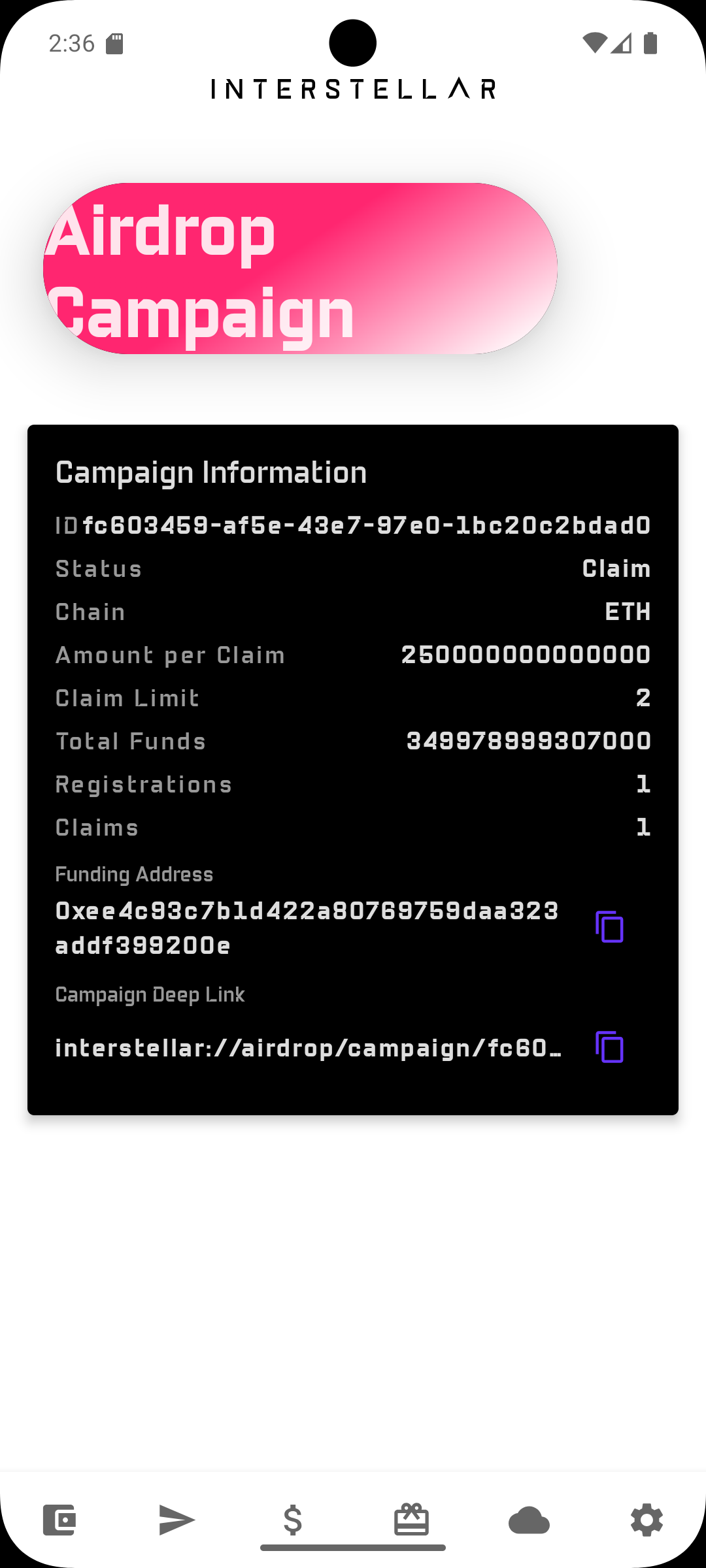
This run uses:
- campaign_id:
fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 - campaign funding address (ETH):
0xee4c93c7b1d422a80769759daa323addf399200e
You will see both repeated throughout the flow.
1) Campaign Status Query (Before Funding)
2026-02-21T12:57:16Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet campaign_info_of STARTED: account=, campaign_id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }
2026-02-21T12:57:16Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet get_campaign_balance STARTED: chain=ETH
2026-02-21T12:57:16Z DEBUG eth_client::client fetch_balance: formated address = "0xee4c93c7b1d422a80769759daa323addf399200e"
2026-02-21T12:57:16Z DEBUG eth_client::client fetch_balance: RPC response = RpcResponse { result: Some("0x0"), error: None }
Status evaluation includes block-based phase boundaries:
2026-02-21T12:57:16Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop evaluate_status: id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }, status=Created, now=6583, reg_end=7848, claim_end=1009149
How to read this
status=Created→ campaign exists but is not yet activatednow=6583→ current parent-chain block numberreg_end=7848→ registration is open until block 7848claim_end=1009149→ claim period ends at block 1009149
2) Funding & Activation
Once the campaign escrow is funded, the wallet triggers fund_campaign to activate it.
2026-02-21T13:01:48Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet fund_campaign STARTED: campaign_id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }
2026-02-21T13:01:48Z DEBUG eth_client::client fetch_balance: formated address = "0xee4c93c7b1d422a80769759daa323addf399200e"
2026-02-21T13:01:48Z DEBUG eth_client::client fetch_balance: RPC response = RpcResponse { result: Some("0x221b262dd8000"), error: None }
The pallet compares required vs actual escrow balance:
2026-02-21T13:01:48Z INFO pallet_airdrop Campaign id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }, required=500046202494800, actual_balance=600000000000000
2026-02-21T13:01:48Z INFO pallet_airdrop::pallet Campaign CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 } funded with 600000000000000 ETH and activated
What this guarantees
- the escrow holds enough funds to cover allocations + fees + margin
- once funded, the campaign becomes eligible for registration / claim according to phase rules
3) Registration (VCA Validation via tx_validation)
When the wallet opens the campaign (e.g., after injecting the deep link in the emulator), it queries campaign metadata and balance:
In this design, registration is not a passive “link opened” event.
It becomes effective when the user performs a VCA one-time-code validation (handled by pallet_tx_validation).
When the user checks their campaign state, the runtime evaluates the campaign status:
2026-02-21T13:05:12Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet get_user_campaign_state STARTED: account=, campaign_id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }
2026-02-21T13:05:12Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop evaluate_status: id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }, status=Registration, now=7057, reg_end=7848, claim_end=1009149
Meaning
- At
now=7057, the campaign is in Registration phase. - The user can register by completing a VCA validation.
4) Transition: Registration → Claim Phase
When the registration window expires, the pallet moves the campaign to the claim phase:
2026-02-21T13:24:07Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop evaluate_status: id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }, status=Registration, now=8192, reg_end=7848, claim_end=1009149
2026-02-21T13:24:07Z INFO pallet_airdrop Campaign id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 } registration expired. Moving to Claim phase.
Meaning
now=8192is afterreg_end=7848→ registration is closed- the campaign is now in Claim phase
Operationally, this is where any configured “waiting / freeze delay before claim” is enforced by phase boundaries. The wallet UI should guide the user accordingly.
5) Claim (Second VCA Validation + External Transfer)
When the user claims the airdrop, claim_airdrop is called.
5.1 Claim start and registration check
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet claim_airdrop STARTED
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet claim_airdrop: taking active claim for user
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet claim_airdrop: checking registration for user in campaign CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }
5.2 VCA validation for the claim
The airdrop pallet calls validate_airdrop_vca, which delegates the digit verification to pallet_tx_validation:
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet validate_airdrop_vca STARTED: account=
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z INFO pallet_tx_validation::pallet [tx-validation] check_input: who = , ipfs_cid = "QmctBo1y4tyKwxpNvqgKUAhpc1quD9qyrKhZXkgZc3rPUU", input_digits = [7, 4]
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z INFO pallet_tx_validation::pallet [tx-validation] check_input: computed_inputs_from_permutation = [4, 9], message_digits = BoundedVec([4, 9], 10)
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z INFO pallet_tx_validation::pallet [tx-validation] TxPass
Key points
ipfs_cid=...ties the claim to the session/circuit material.- The digits are validated against the (randomized) pinpad permutation.
TxPassis the authoritative signal that the VCA validation succeeded.
5.3 Transfer preparation and broadcast (ETH)
Once validated, the pallet performs the external transfer:
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop::pallet transfer_airdrop STARTED: recipient=, amount=250000000000000
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z INFO pallet_tx_manager::pallet [prepare_transaction] START - account=, chain=ETH, amount=Fixed(250000000000000), fee_type=Normal
The ETH client fetches fees and signs an EIP-1559 transaction, then broadcasts it:
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG eth_client::client fetch_latest_base_fee: got: 32
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG eth_client::fee [eth-fee] fee_type=Normal, base_fee=32, priority_fee=1000000 -> max_fee=1000064, max_priority=1000000
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z INFO pallet_tx_manager::pallet [prepare_transaction] Auto-approved transaction broadcast successful: 0x0e5c8ee75eec5b1181e91c3cb7c2fa2ea3ef746b9daaf13dd748b5fd24c9b6aa
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z INFO pallet_airdrop::pallet External transfer successful
Finally, the campaign status is checked to ensure we are in the expected phase:
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop evaluate_status: id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 }, status=Claim, now=8514, reg_end=7848, claim_end=1009149
2026-02-21T13:29:28Z DEBUG pallet_airdrop ensure: id=CampaignId { id: fc603459-af5e-43e7-97e0-1bc20c2bdad0 } status(Claim) == expected(Claim)
What to look for (Quick Checklist)
When troubleshooting or validating a demo run, look for these milestones:
- Created, not funded:
status=Created+fetch_balance ... 0x0 - Funding recognized:
required=... actual_balance=...thenactivated - Registration phase:
status=Registrationwithnow < reg_end - Phase transition:
registration expired. Moving to Claim phase. - Claim attempt:
claim_airdrop STARTED+checking registration for user - VCA success:
[tx-validation] TxPass - External transfer:
broadcast successful: 0x...thenExternal transfer successful
Applies to DOT / BTC / SOL
The same pattern remains:
- campaign lifecycle and phase boundaries (Created → Registration → Claim)
- two human-validated steps (registration VCA + claim VCA)
- bot resistance enforced by
tx_validation
Only these vary per chain:
- fee model and transaction encoding
- address format and clients used (DOT/BTC/SOL client instead of ETH client)
Optional: Front-End Access
You can inspect chain state and transactions via:
- Polkadot.js Apps
- Or your preferred Substrate front-end UI
Notes
- All services run in Docker containers and use local ports
9944,2090, and5001 - This setup replicates the same runtime environment used in hosted testnets but fully self-contained
- Ideal for offline testing, developer evaluation, or deeper inspection of runtime logs
Recovery was introduced in M1 and remains part of the overall testnet scope. All subsequent milestones are designed to remain compatible with the recovery flow, but in M2 we are not re-testing or refining recovery.
The focus of M2 is backend transaction generation and execution. Recovery will be revisited in future milestones (notably M4) and fully integrated with the SDK delivery, where its stability and developer usability can be validated in a realistic context.
This avoids redundant effort at this stage, while ensuring continuity from M1 to later milestones.
This Android application is provided as a technical demonstration of Interstellar’s secure Web3 account infrastructure. It serves as a foundation for the forthcoming Android and iOS SDKs, which are still under active development.
Please note that the current user interface and experience are not representative of the final product. Both UI and UX will be significantly refined to align with Interstellar’s core mission: delivering the highest levels of simplicity and security in mobile self-custody.
If you've jumped straight into the evaluation, we recommend consulting the Milestone 1 documentation for key context. It outlines the core architecture, backend logic, and trusted execution flows implemented in this milestone.
The documentation is modular—feel free to explore only the sections most relevant to your review or interest.
You can also use the search bar (top right corner) to locate specific topics quickly. Helpful keywords include:
VHDL,circuits,garbled,TEE,integritee,SE attestationNFC,VCA,recovery,threshold,trusted UXcomparison,passkey,ledger,authentication,compliance,security,ATT&CK